Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption or symmetric key or single-key encryption is an encryption system which the encryption and the decryption processes are preforms using the same key.
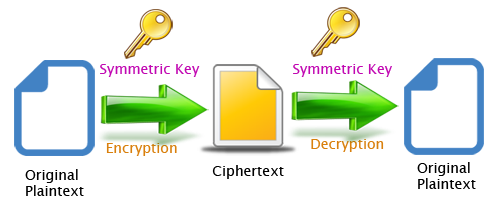
- Plaintext (P) The original message or data, the plaintext is an input to the encryption algorithm.
- Encryption algorithm (E) This algorithm preforms various substitution and transposition on the plaintext and produces the ciphertext.
- Ciphertext (C) Is the output produced by the encryption algorithm , the ciphertext is scrambled message and it is appears like a random stream of data.
- Encryption key (K) Encryption key or secret key is a value that independent of the plaintext. Encryption key is an input to the encryption algorithm. The encryption algorithm will produces a different with different keys.
- Decryption algorithm (D) This algorithm is a reverse of the the encryption algorithm , and it takes ciphertext and the encryption key as input and produces the plaintext as output.
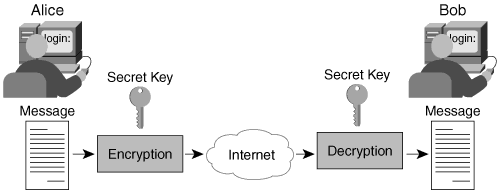
Alice want to send encrypted message to Bob and both have the secret key which generated by the encryption algorithm or by a third-party software, this process will work as the following steps:
- Encryption algorithm E (on Alice’s computer) takes the plaintext P, and the secret key Kand generates a ciphertext C. C = E(P,k)
- The ciphertext C will be transferred via internet
- Decryption algorithm D (on Bob’s computer) takes the ciphertext and the secret key K (the same key) and regenerate the original plaintext P again. P = D(C,K)
Hint 1: The encryption key is independent of the plaintext or the encryption algorithm.
Hint 2: The sender and receiver must have copies of the encryption key and they must secure that key.
Hint 3: We do not need to keep the encryption algorithm secure because it is impractical to decrypt a ciphertext by only using the decryption algorithm , and that’s the same for the encryption algorithm.
Hint 4: Key exchange must be done via a secured channel.